LADI-III
Quasi-Laue diffractometer
A quasi-Laue diffractometer for macromolecular crystallography
The quasi-Laue diffractometer LADI-III is used for single crystal neutron diffraction studies at high resolution (1.5 – 2.5 Å) of biological macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, providing unique information regarding hydrogen that is complementary to X-ray crystallography. Locating the positions of hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) atoms and protons/deuterons (H+/D+) reveals important information on protonation, H-bonding and hydration. These details allow a more complete understanding of a macromolecule’s specific function, such as reaction pathways of enzymes, and can assist in structure-guided drug-design. Neutron macromolecular crystallography is unique in its ability to provide these invaluable details at room-temperature, and without radiation damage.
Applications
Neutron macromolecular crystallography projects typically aim to address questions concerning:
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Small-molecule (e.g. drug, ligand) binding interactions
- Rational drug-design
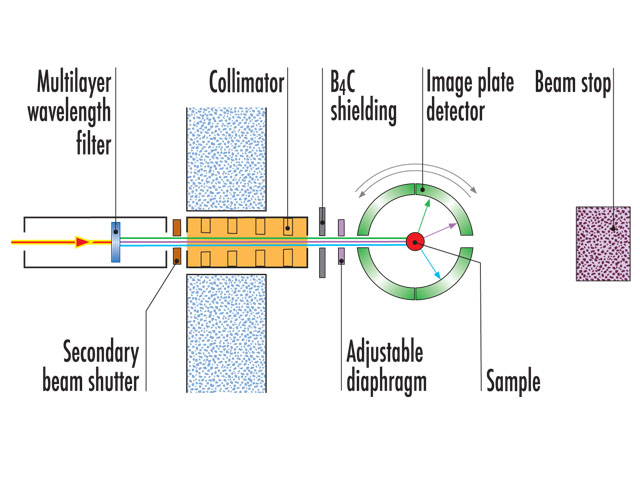
Instrument layout
LADI-III uses a large cylindrical area detector composed of neutron-sensitive image-plates, which completely surround the crystal and allows large numbers of reflections to be recorded simultaneously. Data are collected using quasi-Laue methods in order to provide a rapid survey of reciprocal space, while reducing the background on the detector compared to use of the full white beam.