Page 161 - Neutrons for Sciences and Society
P. 161
Chapter 6: The start of research activities and the arrival of the British
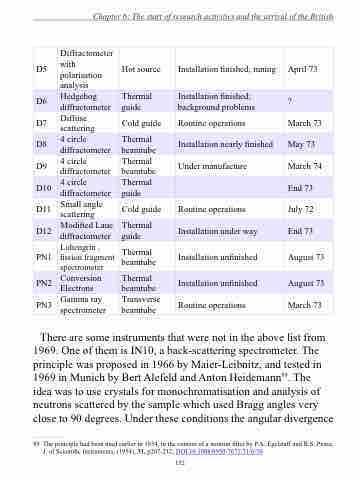
D5
Diffractometer with polarisation analysis
Hot source
Installation finished; tuning
April 73
D6
Hedgehog diffractometer
Thermal guide
Installation finished; background problems
?
D7
Diffuse scattering
Cold guide
Routine operations
March 73
D8
4 circle diffractometer
Thermal beamtube
Installation nearly finished
May 73
D9
4 circle diffractometer
Thermal beamtube
Under manufacture
March 74
D10
4 circle diffractometer
Thermal guide
End 73
D11
Small angle scattering
Cold guide
Routine operations
July 72
D12
Modified Laue diffractometer
Thermal guide
Installation under way
End 73
PN1
Lohengrin , fission fragment spectrometer
Thermal beamtube
Installation unfinished
August 73
PN2
Conversion Electrons
Thermal beamtube
Installation unfinished
August 73
PN3
Gamma ray spectrometer
Transverse beamtube
Routine operations
March 73
There are some instruments that were not in the above list from 1969. One of them is IN10, a back-scattering spectrometer. The principle was proposed in 1966 by Maier-Leibnitz, and tested in 1969 in Munich by Bert Alefeld and Anton Heidemann89. The
idea was to use crystals for monochromatisation and analysis of neutrons scattered by the sample which used Bragg angles very close to 90 degrees. Under these conditions the angular divergence
89 The principle had been used earlier in 1954, in the context of a neutron filter by P.A. Egelstaff and R.S. Pease, J. of Scientific Instruments, (1954), 31, p207-212; DOI 10.1088/0950-7671/31/6/30
152