Page 70 - Neutrons for Sciences and Society
P. 70
Neutrons for Science
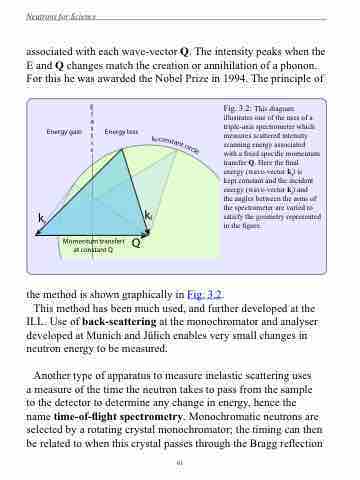
associated with each wave-vector Q. The intensity peaks when the E and Q changes match the creation or annihilation of a phonon. For this he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1994. The principle of
Energy gain
Energy loss
Fig. 3.2: This diagram illustrates one of the uses of a triple-axis spectrometer which measures scattered intensity scanning energy associated
with a fixed specific momentum transfer Q. Here the final energy (wave-vector kf) is
kept constant and the incident energy (wave-vector ki) and
the angles between the arms of the spectrometer are varied to satisfy the geometry represented in the figure.
kf Momentum transfert
ki
at constant Q
Q
the method is shown graphically in Fig. 3.2.
This method has been much used, and further developed at the
ILL. Use of back-scattering at the monochromator and analyser developed at Munich and Jülich enables very small changes in neutron energy to be measured.
Another type of apparatus to measure inelastic scattering uses
a measure of the time the neutron takes to pass from the sample to the detector to determine any change in energy, hence the name time-of-flight spectrometry. Monochromatic neutrons are selected by a rotating crystal monochromator; the timing can then be related to when this crystal passes through the Bragg reflection
61
Elastic
k
c
o
f
n
s
t
a
n
t
c
i
r
c
l
e